Web projects need to consider frontend storage solutions due to HTTP statelessness, frontend performance, and data sharing when SPA application pages jump. Each solution has its own characteristics, and understanding them is essential for reasonable selection and use. Here is a summary.
Storage Solutions
- cookie
- sessionStorage
- localStorage
- indexedDB
Web SQL
You can still see Web SQL in Chrome browser developer tools, but it is not part of the HTML5 specification and is not supported by Firefox, so it is not recommended.
Solution Differences
For the above solutions, here are the differences from various dimensions.
Storage Size
- cookie: 4kb
- sessionStorage: 2.5-10MB, varies by browser
- localStorage: 2.5-10MB, varies by browser
- indexedDB: > 250MB, varies by browser
Expiration Time
- Cookies with an expiration time are automatically cleared when they expire
- sessionStorage is cleared when the browser is closed
- Note that different tabs and windows have different sessions. However, if you copy a page A directly in the browser, you will find that the sessionStorage default value is from the previous page, but it is still an independent session storage.
- localStorage is permanently stored
- indexedDB is permanently stored
Interaction with Server
- Cookies have interaction; sessionStorage, localStorage, and indexedDB do not
- Cookies are carried in every request [except cross-domain asynchronous requests], so do not make cookie data too heavy, which can cause large request packets
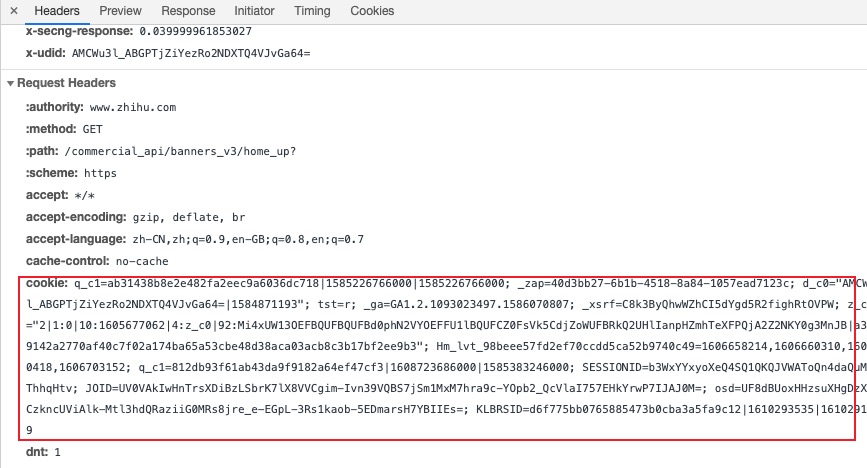
Synchronous vs Asynchronous
- indexedDB operations are asynchronous; cookie, sessionStorage, and localStorage are all synchronous
Access Policy
- cookie, sessionStorage, indexedDB, and localStorage comply with the Same-Origin Policy and can be accessed.
- Cookies can be shared across different origins by setting a domain.
Application Scenarios
- cookie: Login tokens, short-term storage
- sessionStorage: Short-term storage without communication with the backend and size requirements
- localStorage: Long-term storage
- indexedDB: Large amounts of structured data, long-term storage

