To improve performance, websites can use CDN, but do you really understand CDN? Here we sort out the principles to strengthen understanding.
Concept
Content Delivery Network (CDN) refers to a computer network system connected to each other through the Internet that uses servers closest to each user to send music, pictures, videos, applications, and other files to users more quickly and reliably. This provides high performance, scalability, and low-cost network content delivery to users.
The above is from Wikipedia as a basic concept. Next, let’s understand the implementation principle of CDN.
Principle
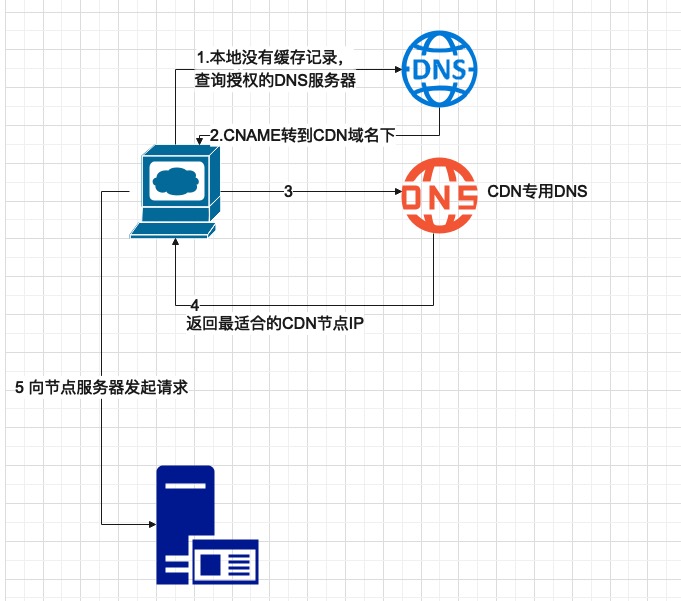
From the above figure, we can see the key technologies implemented by CDN services:
CNAME- When configuring CDN resources, the domain name configured in the webpage is not the domain name provided by the CDN service, but a custom domain name. This custom domain name actually exists as an alias of the CDN resource domain name.- CDN services need to have their own
DNSbecause domain name resolution to IP is required. - Load balancing capabilities (Global Server Load Balance, abbreviated as
GSLB) - Normally, when we resolve domain names to IPs, we can understand them as static. However, to have load balancing capabilities, the DNS resolution to IP becomes a dynamic process. This allows the CDN to return the most suitable CDN node IP, enabling users to access nearby servers.
OK, so now we understand CDN.
DNS-prefetch
As we know, domain name to IP resolution takes time. To improve speed, we can use DNS prefetching for these cross-domain static resources in the web. Why does this make it faster? Because Chrome will start a dedicated thread for DNS-prefetching.
Generally speaking, reasonable DNS prefetching can bring 50ms ~ 300ms improvement to page performance. Someone has done statistics on this aspect.
<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//static.1991421.cn">
Benefits of CDN
CDN ultimately provides users with good resource access speed, but in actual use, there are many other benefits besides this. For example, it can also save bandwidth. For non-homologous sites, resources need to be reloaded repeatedly, and our CDN as a third-party resource can also avoid the waste of repeated resource loading.
Final Thoughts
Understanding not only what it is, but also why it is, makes it interesting and allows us to better master technology.

